gelatenous skin premature baby|Biomarkers of neonatal skin barrier adaptation reveal : Baguio The microbiota refers to the microorganismsthat colonise the human body. Infants are thought to be virtually sterile at birth and acquire their microbiota over time, reaching mature colonisation at 2–3 years of age. The development of the neonatal microbiota is influenced by the delivery method . Tingnan ang higit pa The Department of Education implements non-formal education programs through the ALS. Non-formal education is defined by UNESCO as “education that is institutionalized, intentional and planned by an education provider. The defining characteristic of non-formal education is that it is an addition, alternative and/or a complement to formal .
gelatenous skin premature baby,The microbiota refers to the microorganismsthat colonise the human body. Infants are thought to be virtually sterile at birth and acquire their microbiota over time, reaching mature colonisation at 2–3 years of age. The development of the neonatal microbiota is influenced by the delivery method . Tingnan ang higit paPremature infants are babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy, with further classification by gestationalage as preterm (32–37 . Tingnan ang higit pa
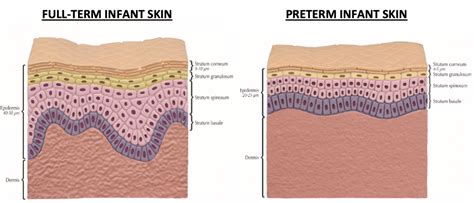
The epidermis develops from a single layer of cells to three layers by 11 weeks gestation, and to 4–5 layers by 23 weeks. The stratum corneum layer of the epidermis . Tingnan ang higit pa

Premature infants may require admission to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for further care due to their complicated medical problems. Infants admitted to the NICU . Tingnan ang higit pagelatenous skin premature baby Biomarkers of neonatal skin barrier adaptation reveal Premature infants may require admission to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) for further care due to their complicated medical problems. Infants admitted to the NICU . Tingnan ang higit pa
Impermeable wraps may be required to reduce heat loss in the first minutes after birth of a premature baby. Semipermeable wraps may then be used for days to weeks to reduce water and electrolyte loss through the skin. Although adhesive dressings . Tingnan ang higit paSkin problems in the premature baby. Babies born earlier than 37 weeks are considered premature. Low birth weight and breathing problems are well-known concerns, but skin .
Premature infant skin is thinner than that of full-term newborns and looks transparent or even gelatinous in extremely immature infants. Typically, the ruddy appearance is due to fewer layers of stratum corneum; thus, skin .
Given that infant skin is more hydrated than adult skin, the skin microbiome of newborns resembles the microbiome of moist skin sites in adults. Moreover, in . Results. Forty proteins were differentially expressed in FT infant skin, 38 in LPT infant skin, and 12 in PT infant skin compared with adult skin at T1. At T2, 40 . The skin of preterm infants is a delicate organ with critical structural and functional differences as compared to term born infants. Unique features contribute to an increased.Most guidelines on neonatal skin care emphasize issues pertaining to healthy, term infants. Few address the complex task of skin barrier maintenance in preterm, very preterm, and .
The skin of preterm and term newborn babies has distinct differences from juvenile and adult skin. An understanding of the nature of neonatal skin, the .
Chest TEWL was significantly higher for premature versus full-term infants over 2 weeks, suggesting that even 7–8 weeks after birth, skin integrity is poorer in .Skin development in preterm infants has reproducible milestones. Significant structural changes occurring around 28-30 weeks may improve barrier function, with implications .Objective: To evaluate the effects of gestational age (GA) and postnatal age on skin barrier integrity by comparing premature infants at full-term corrected age with infants born at term. Study design: Parallel comparison of chest skin in 36 premature infants with 39 full-term infants using daily measures of transepidermal water loss (TEWL), skin pH, .
We sought to qualitatively and quantitatively describe the histopathologic patterns of skin development in preterm infants. Methods: Autopsy skin samples were examined for 48 liveborn preterm infants born at 18+ to 36 weeks, and control groups of term neonates and older infants/children. Quantitative variables included thickness of the stratum .Biomarkers of neonatal skin barrier adaptation reveal • 22-23 Week Premature Infants • Approximately 1 ft long • Weigh between 0.9-1.1 lbs • Skin is gelatinous, sticky, and can tear easily • Doctors often do not attempt resuscitation • Prior Group’s Model • Skin is more accurate than models on the market • Needs limbs for IV insertion • Needs improved chest cavity for accurate .
Skin to skin contact with a care giver, known as kangaroo mother care, should start immediately after birth, without any initial period in an incubator, the World Health Organization has recommended.1 The preterm and low birthweight infant guidelines advise that skin to skin contact can be initiated before the infant is clinically stable, .multiple locations for IV insertions [5]. At just 2-3 weeks away from the team’s desired infant mannequin, Premature Anne is still significantly bigger than a 22-23 week premature baby. Further, the skin does not aPcrcuorbatleelym re pSretsaetnet tmhee tnhitn, gelatinous skin of an infant at 22-23 week gestational age.Premature infant skin is thinner than that of full-term newborns and looks transparent or even gelatinous in extremely immature infants. Typically, the ruddy appearance is due to fewer layers of stratum corneum; thus, skin color is a poor tool for assessing oxygenation of very immature infants.A premature baby’s skin is up to two times thinner than a full-term baby’s skin. Their skin barrier is usually less developed, making it more delicate and vulnerable to infections and irritation. A preemie’s skin usually takes a few weeks to . WHO today launched new guidelines to improve survival and health outcomes for babies born early (before 37 weeks of pregnancy) or small (under 2.5kg at birth). The guidelines advise that skin to skin contact with a caregiver – known as kangaroo mother care – should start immediately after birth, without any initial period in an .
The significance of preterm birth lies in the complications of prematurity sustained by the infant and the impacts of these complications on the infant’s survival and subsequent development. Many clinical research studies of infants born preterm limit their outcomes to neonatal mortality and morbidity. Complications and the disturbance of normal .aesthetic outcomes are considered. In addition, the high-level medical needs of extremely preterm infants demand skin-level medical interventions that too often result in unintended skin harm. Purpose: We describe the use of a harm prevention, or consequence-centered, approach to skin care, which facilitates safer practice for extremely premature infants. .An infant born before 37 weeks of gestation is considered preterm. In 2021 in the United States, 10.48% of births were preterm (1), and in 2018, 26.53% of births were early term (significantly increased from 26% in 2017) (2).Preterm infants, even late preterm infants who are the size of some full-term infants, have increased morbidity and mortality .
INTRODUCTION. Premature infants are live-born babies delivered before 37 complete weeks of gestation [1,2].Their skin is still thin, reddish, and wrinkled with a small amount of subcutaneous fat due to immaturity [].Thus, the skin is softer and more pliable, resulting in a greater degree of skin laxity and mobility than a full-term infant .the preterm infant skin with focus on: (1) barrier develop-ment and function, (2) skin microbiome interactions, and (3) potential clinical implications for preterm skin care practices and infection prevention measures. Unique Features of Preterm Infants’ Skin Key Structural Differences of Skin between Preterm and Term InfantsIf you’re feeding them baby formula, you could try giving them a little cooled, boiled water between milk feeds. Baby massage may also help with a baby’s digestion issues. Find out more about baby massage. If your baby’s constipation doesn’t get better, the GP will examine them and may give them laxatives to help them poo. RefluxMeconium is a newborn baby’s first feces, usually passing within the first 24 to 48 hours of birth.. This can be dark greenish to black and typically has a tar-like texture. It’s usually made up of materials ingested by your infant in the womb, such as mucus, amniotic fluid, bile, water, skin cells, etc. Abstract. The skin of preterm infants is a delicate organ with critical structural and functional differences as compared to term born infants. Unique features contribute to an increased susceptibility to injury, infection, thermal instability, and water loss. During rapid, often accelerated adaption of the physical barrier function of preterm .

How Your Premature Baby Looks. The earlier your baby arrives, the smaller she will be, the larger her head will seem in relation to the rest of her body, and the less fat she will have. With so little fat, her skin will seem thinner and more transparent, allowing you actually to see the blood vessels beneath it.
gelatenous skin premature baby|Biomarkers of neonatal skin barrier adaptation reveal
PH0 · The Delicate Skin of Preterm Infants: Barrier Function,
PH1 · Skin Problems in the Premature Baby
PH2 · Skin Physiology of the Neonate and Infant: Clinical Implications
PH3 · Preterm Infant Skin Structure Is Qualitatively and
PH4 · Premature infant skin barrier maturation: status at full
PH5 · Premature infant skin and care
PH6 · Physiological skin conditions of preterm and term neonates
PH7 · Neonatal Skin Care: The Scientific Basis for Practice
PH8 · Neonatal Skin Care: The Scientific Basis for Practice
PH9 · Evidence
PH10 · Biomarkers of neonatal skin barrier adaptation reveal